Month: Mar 2022
Conductive Tapes – A Selection Guide
Conductive tapes are flexible adhesives that conduct current on one or both sides. These tapes are a useful and cost-effective option for electronic assembly, especially in shielding or grounding applications.
Conductive tape offers many advantages over other assembly methods such as soldering or mechanical fastening. Tapes are flexible, easy to apply, and offer better performance in settings with extreme temperatures or frequent vibrations.
At Robert McKeown Company, we offer a full range of conductive tapes for clients seeking these benefits for their electronic assemblies. As a long-time supplier of high-performance electronics materials, we can work with you to determine the best adhesive tape solution for your needs.
CONDUCTIVE TAPE TYPES
Conductive tapes can be classified in several ways:
- Conductive Adhesive vs. Non-Conductive Adhesive. Tapes with conductive adhesive conduct electricity on both the top and the bottom. The polymers that make these tapes sticky contain tiny, embedded metal particles that conduct current. By contrast, some conductive tapes do not have these embedded components, so they only conduct current on the non-adhesive surface.
- Isotropic vs. Anisotropic. Isotropic tapes conduct current in every direction while anisotropic adhesives conduct along only one axis.
- Material. Conductive tapes can be made from many different materials, including copper, aluminum, and conductive alloys.
Robert McKeown Company offers performance CHO-FOIL tapes in several material options with conductive and non-conductive adhesives:
- Copper Foil Tape. Copper is highly desirable for electrical applications because of its excellent conductivity, which is second only to silver. Copper is a particularly good choice for both grounding and shielding applications because it reliably blocks both magnetic and electrical waves for maximum performance.
- Aluminum Foil Tape. Although its conductivity is slightly lower than copper’s, aluminum tapes offer excellent electrical performance and shielding characteristics. Aluminum tape also tends to be more cost-effective than copper or tinned copper tapes.
- Tinned Copper Foil Tape. Tinned copper foil has similar electrical properties to copper foil, but the tin content makes the tape more resistant to humidity and extreme temperatures. Unlike unalloyed copper, tinned copper won’t oxidize in these more difficult environments, so it is a better choice if durability is a concern.
Before purchasing conductive tape, it’s important to understand these distinctions to ensure you get the results you’re expecting.
COMMON APPLICATIONS FOR CONDUCTIVE ADHESIVES
Conductive tapes have many uses, but the most common involve shielding and grounding. For instance, they are often used to attach EMI and RFI shields to electronic devices. They can also be used to pass current to substrates that cannot be soldered or to create corrosion-resistant ground contacts, among other applications.
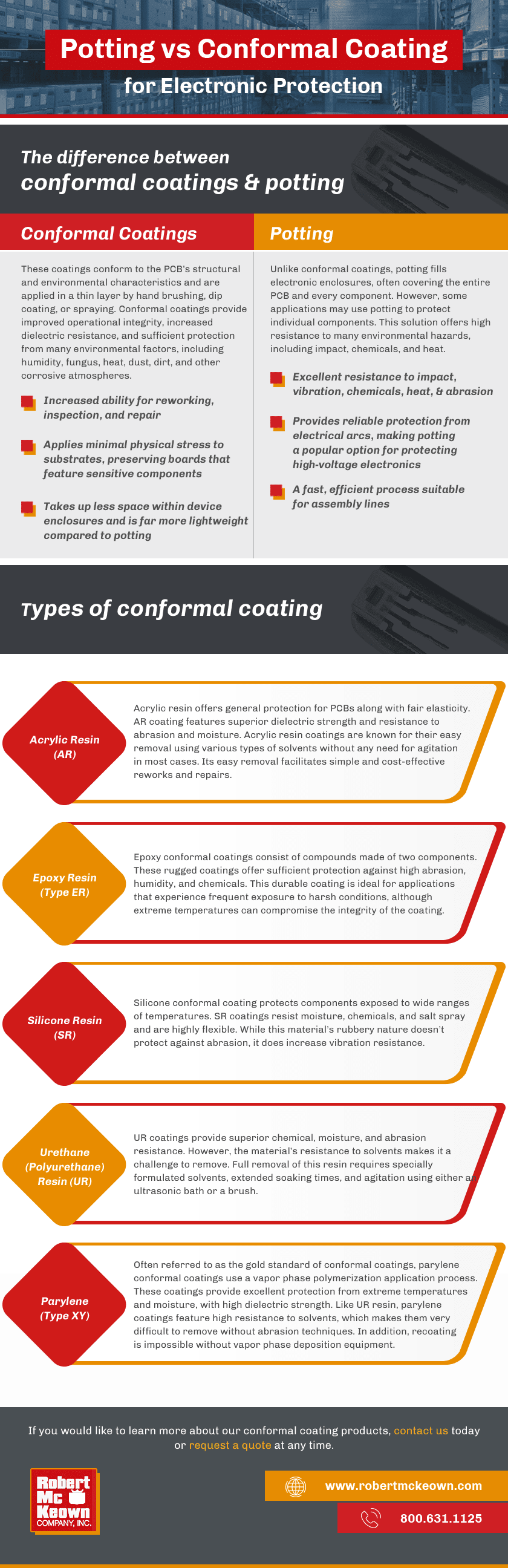
Potting vs Conformal Coating for Electronic Protection
Electronic components, including printed circuit boards (PCBs), often sustain damage and wear as a result of exposure to harsh environments. Conformal coatings offer protection for these components from a variety of potentially damaging environmental factors, including dust, moisture, chemicals, and salt, along with mechanical abrasion and changes in temperature. With the help of reliable conformal coating, electronics won’t be susceptible to corrosion and other types of damage.
The Difference Between Conformal Coatings & Potting
Both potting and conformal coatings protect PCBs and other electronic components but differ in functionality and application. The following are the key differences between these two types of protective materials:
Conformal Coatings
These coatings conform to the PCB’s structural and environmental characteristics and are applied in a thin layer by hand brushing, dip coating, or spraying. Conformal coatings provide improved operational integrity, increased dielectric resistance, and sufficient protection from many environmental factors, including humidity, fungus, heat, dust, dirt, and other corrosive atmospheres.
Some of the advantages of using conformal coatings include:
- Increased ability for reworking, inspection, and repair
- Applies minimal physical stress to substrates, preserving boards that feature sensitive components
- Takes up less space within device enclosures and is far more lightweight compared to potting
Potting
Unlike conformal coatings, potting fills electronic enclosures, often covering the entire PCB and every component. However, some applications may use potting to protect individual components. This solution offers high resistance to many environmental hazards, including impact, chemicals, and heat.
Potting offers a few key benefits, such as:
- Excellent resistance to impact, vibration, chemicals, heat, and abrasion
- Provides reliable protection from electrical arcs, making potting a popular option for protecting high-voltage electronics
- A fast, efficient process suitable for assembly lines
Types of Conformal Coating
Depending on the needs of the application, there are several types of conformal coating materials available, including:
Acrylic Resin (AR)
Acrylic resin offers general protection for PCBs along with fair elasticity. AR coating features superior dielectric strength and resistance to abrasion and moisture. Acrylic resin coatings are known for their easy removal using various types of solvents without any need for agitation in most cases. Its easy removal facilitates simple and cost-effective reworks and repairs.
Epoxy Resin (Type ER)
Epoxy conformal coatings consist of compounds made of two components. These rugged coatings offer sufficient protection against high abrasion, humidity, and chemicals. This durable coating is ideal for applications that experience frequent exposure to harsh conditions, although extreme temperatures can compromise the integrity of the coating.
Silicone Resin (SR)
Silicone conformal coating protects components exposed to wide ranges of temperatures. SR coatings resist moisture, chemicals, and salt spray and are highly flexible. While this material’s rubbery nature doesn’t protect against abrasion, it does increase vibration resistance.
Urethane (Polyurethane) Resin (UR)
UR coatings provide superior chemical, moisture, and abrasion resistance. However, the material’s resistance to solvents makes it a challenge to remove. Full removal of this resin requires specially formulated solvents, extended soaking times, and agitation using either an ultrasonic bath or a brush.
Parylene (Type XY)
Often referred to as the gold standard of conformal coatings, parylene conformal coatings use a vapor phase polymerization application process. These coatings provide excellent protection from extreme temperatures and moisture, with high dielectric strength. Like UR resin, parylene coatings feature high resistance to solvents, which makes them very difficult to remove without abrasion techniques. In addition, recoating is impossible without vapor phase deposition equipment.
Conformal Coatings at Robert McKeown Company, Inc.
Conformal coatings help protect PCBs from many types of hazardous environments, maximizing their longevity. At Robert McKeown Company, Inc., we offer custom conformal coating solutions based on our clients’ unique requirements. Our experts will help select the right materials for your electronic components to meet any specifications.
If you would like to learn more about our conformal coating products, contact us today or request a quote at any time.