Author: Robert McKeown
Benefits of Potting Electronics
To provide electronic components with sufficient protection against an array of hazards, many fabricators use a process called potting. By potting electronics, you better safeguard electronic wiring, parts, and devices from premature failure so as not to compromise electronic systems. Learn more about potting in electronics, how it works, and its benefits and applications.
What Is Potting in Electronics?
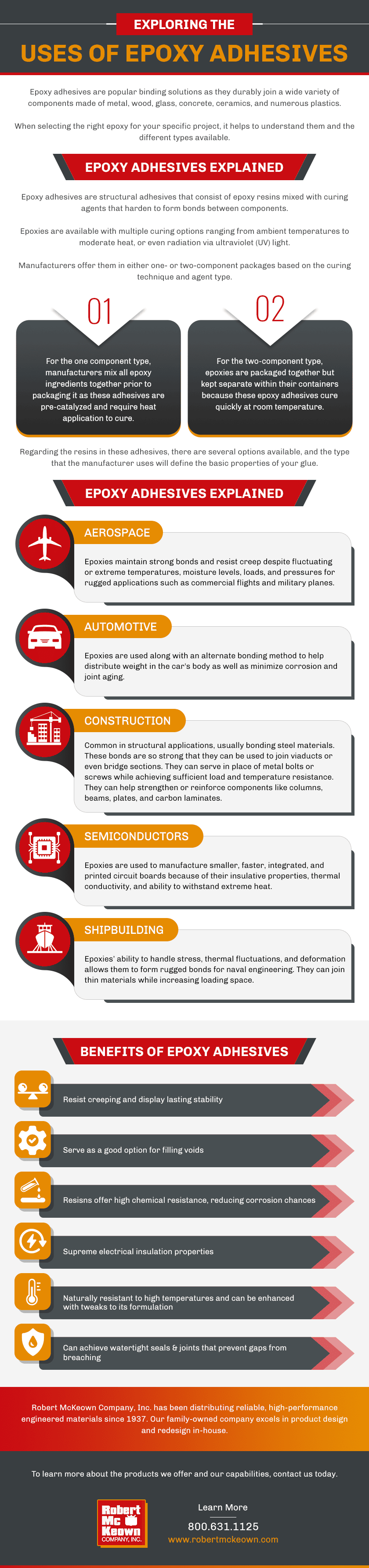
Exploring the Uses of Epoxy Adhesives
Epoxy adhesives are popular binding solutions as they durably join a wide variety of components made of metal, wood, glass, concrete, ceramics, and numerous plastics. To select the right epoxy for your specific project, it helps to understand them and the different types available. Read on to learn about epoxy uses and the advantages these adhesives offer diverse applications.
Epoxy Adhesives Explained
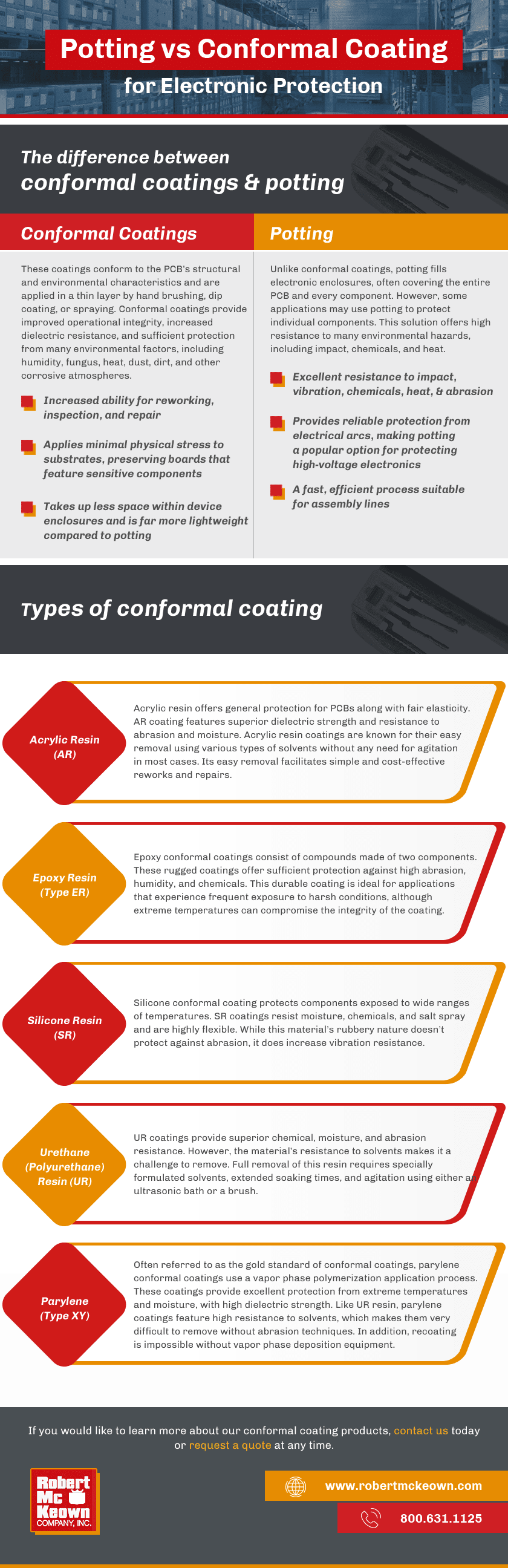
Potting vs Conformal Coating for Electronic Protection
Electronic components, including printed circuit boards (PCBs), often sustain damage and wear as a result of exposure to harsh environments. Conformal coatings offer protection for these components from a variety of potentially damaging environmental factors, including dust, moisture, chemicals, and salt, along with mechanical abrasion and changes in temperature. With the help of reliable conformal coating, electronics won’t be susceptible to corrosion and other types of damage.
The Difference Between Conformal Coatings & Potting
Both potting and conformal coatings protect PCBs and other electronic components but differ in functionality and application. The following are the key differences between these two types of protective materials:
Conformal Coatings
These coatings conform to the PCB’s structural and environmental characteristics and are applied in a thin layer by hand brushing, dip coating, or spraying. Conformal coatings provide improved operational integrity, increased dielectric resistance, and sufficient protection from many environmental factors, including humidity, fungus, heat, dust, dirt, and other corrosive atmospheres.
Some of the advantages of using conformal coatings include:
- Increased ability for reworking, inspection, and repair
- Applies minimal physical stress to substrates, preserving boards that feature sensitive components
- Takes up less space within device enclosures and is far more lightweight compared to potting
Potting
Unlike conformal coatings, potting fills electronic enclosures, often covering the entire PCB and every component. However, some applications may use potting to protect individual components. This solution offers high resistance to many environmental hazards, including impact, chemicals, and heat.
Potting offers a few key benefits, such as:
- Excellent resistance to impact, vibration, chemicals, heat, and abrasion
- Provides reliable protection from electrical arcs, making potting a popular option for protecting high-voltage electronics
- A fast, efficient process suitable for assembly lines
Types of Conformal Coating
Depending on the needs of the application, there are several types of conformal coating materials available, including:
Acrylic Resin (AR)
Acrylic resin offers general protection for PCBs along with fair elasticity. AR coating features superior dielectric strength and resistance to abrasion and moisture. Acrylic resin coatings are known for their easy removal using various types of solvents without any need for agitation in most cases. Its easy removal facilitates simple and cost-effective reworks and repairs.
Epoxy Resin (Type ER)
Epoxy conformal coatings consist of compounds made of two components. These rugged coatings offer sufficient protection against high abrasion, humidity, and chemicals. This durable coating is ideal for applications that experience frequent exposure to harsh conditions, although extreme temperatures can compromise the integrity of the coating.
Silicone Resin (SR)
Silicone conformal coating protects components exposed to wide ranges of temperatures. SR coatings resist moisture, chemicals, and salt spray and are highly flexible. While this material’s rubbery nature doesn’t protect against abrasion, it does increase vibration resistance.
Urethane (Polyurethane) Resin (UR)
UR coatings provide superior chemical, moisture, and abrasion resistance. However, the material’s resistance to solvents makes it a challenge to remove. Full removal of this resin requires specially formulated solvents, extended soaking times, and agitation using either an ultrasonic bath or a brush.
Parylene (Type XY)
Often referred to as the gold standard of conformal coatings, parylene conformal coatings use a vapor phase polymerization application process. These coatings provide excellent protection from extreme temperatures and moisture, with high dielectric strength. Like UR resin, parylene coatings feature high resistance to solvents, which makes them very difficult to remove without abrasion techniques. In addition, recoating is impossible without vapor phase deposition equipment.
Conformal Coatings at Robert McKeown Company, Inc.
Conformal coatings help protect PCBs from many types of hazardous environments, maximizing their longevity. At Robert McKeown Company, Inc., we offer custom conformal coating solutions based on our clients’ unique requirements. Our experts will help select the right materials for your electronic components to meet any specifications.
If you would like to learn more about our conformal coating products, contact us today or request a quote at any time.
A Guide to ESD Grounding Methods
In an ever-so technological world, working with highly sensitive electronic devices has become increasingly common across a range of businesses. With that comes certain dangers, such as electrostatic discharge (ESD). ESD refers to the sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects caused by instances such as a short or breakdown.
ESD poses life-threatening dangers to workers; therefore, it is crucial to implement the proper ESD grounding methods. ESD grounding not only improves workplace safety but it’s also an important component of static control.
Developing ESD Grounding Requirements
Developing a widespread policy on how employees should ground themselves while working can be an invaluable step in boosting workplace safety and preventing product damage. Determining ESD grounding requirements for your facility depends on where grounding is needed. The policy could cover areas such as work benches, manufacturing floors, packing and shipping centers, research and development labs, clean rooms, and more.
Other key factors to consider when determining the ESD grounding requirements of a facility include the type of work taking place and the size of the workspace. For example, smaller companies can typically follow basic ESD grounding requirements while larger companies may need to implement stricter guidelines.
The Different Types of ESD Grounding Methods
There are several ESD grounding methods companies can use to protect products and personnel. Implementing the following precautions ensures worker safety when installing or handling electrostatic-sensitive devices:
ESD Wrist Strap
ESD wrist straps are connected by a ground cord to an unpainted surface or grounded workstation. When worn, the straps conduct static electricity from your body to the ground, electrically bonding you with your work area. Doing this prevents static electricity from circulating on or around your body. To ensure proper grounding, it is critical that the strap be snug against the skin.
ESD Mats
Similar to ESD wrist straps, ESD mats are antistatic surfaces that eliminate static electricity by electrically bonding, or grounding, objects or people standing on top of them. Depending on your particular needs, these mats can be either static dissipative or conductive. ESD mats can be placed on tables or floors, and the most common way to ground these areas is by connecting the mats to an electrical outlet via a grounding cable.
Heel Strap, Toe Strap, or Boot Strap
Shoe grounders, such as heel, toe, and boot straps, are commonly used at standing workstations. They work to ground insulative barriers between your feet and the facility you are working in. Wearing the straps on both feet when standing on dissipating floor mats or conductive floors will provide full grounding protection.
Prioritize ESD Grounding with Robert McKeown Inc.
Implementing proper ESD grounding techniques doesn’t have to be a hard and complicated process. With the simple methods outlined above, companies of any size and specialization can work towards a safer work environment for their employees.
Robert McKeown can help with exactly that! We offer a variety of ESD solutions designed to protect against the harmful effects of ESD. Since 1937, we have been a world-class distributor of engineered materials, with a proven track record of reputable, reliable, and high-quality grounding materials that can help change the way your business operates.
For more information about our ESD grounding solutions, contact us or request a quote today.
A Closer Look at Thermal Radical Cure Adhesives for the Electronics Industry
Thermal radical cure (TRC) adhesives are 100% solid formulations based on UV curable resins. This type of adhesive is commonly as hot melt and semi-structural adhesives. These adhesives were created to harness some of the best features of traditional silicone adhesives while eliminating or reducing many of the drawbacks.
This blog post will discuss why thermal radical curing technology is beneficial, discuss the properties of these adhesives, and offer examples of common applications.
WHY USE TRC TECHNOLOGY?
There are many benefits offered by thermal radial curing technology. Some of the primary benefits include:
- Enhanced adhesive performance. The adhesion strength of TRC adhesives is retained across a broad temperature range and throughout a variety of adverse conditions, such as water immersion, salt water exposure, and other corrosive environments.
- Design flexibility. TRC adhesives provide adhesion to a wide range of surfaces. They adhere to plastics, metals, cured silicones, wet substrates, and more. These adhesives will bond with most traditional and alternative materials, enabling improved performance and many new design opportunities.
- Cost control. TRC adhesives facilitate cost savings in the form of reduced energy expenditures and streamlined production processes. They cure much faster than standard silicone adhesives by reducing the heat-up time and cutting the cure down to as little as three minutes.
HOW EXACTLY DO TRC ADHESIVES WORK?
TRC adhesives provide reliable adhesion with a comprehensive array of metals, ceramics, and plastics—even those that haven’t experienced good adhesion with more traditional silicone-based adhesives. Once the adhesive is fully cured, the substrate materials benefit from strong but flexible bonds. With thermal curing processes, these adhesives significantly reduce curing time without sacrificing adhesion strength.
Cationically curable resins and free-radical curable unsaturated esters are the two most common resins used for creating UV-curable adhesives. Cation resins are typically more expensive, but offer better overall performance, higher heat resistance, less shrinkage, and superior strength. Free-radical type adhesives feature reduced properties in comparison, but cure much faster.
TRC APPLICATIONS
There are many use cases for TRC adhesives within the electronics industry. Examples may include:
- Housing assembly
- Attaching connectors to substrates
- Adhering sensors and electronic control units to substrates
- Facilitating power supply and energy conversion
More advanced assembly applications for TRC adhesives may include:
- Engine or transmission control units
- Power control units
- Sensors
- Lighting modules
- Printed circuit boards
TRC ADHESIVES FROM ROBERT MCKEOWN, INC.
TRC adhesives are cost-effective, offer strong and reliable adhesion, and work with a comprehensive range of surface types and materials. The application potential for these adhesives is nearly limitless, especially in sectors such as automotive, electronics, and general manufacturing.
At Robert McKeown, we partner with Dow, a global leader in adhesives and sealants, to provide thermal radical cure adhesive solutions. We’re happy to offer a sample of EA-7100 TRC adhesive from Dow so you can test it in your application. Please contact us today to obtain a sample or with any questions about any of our products and services.
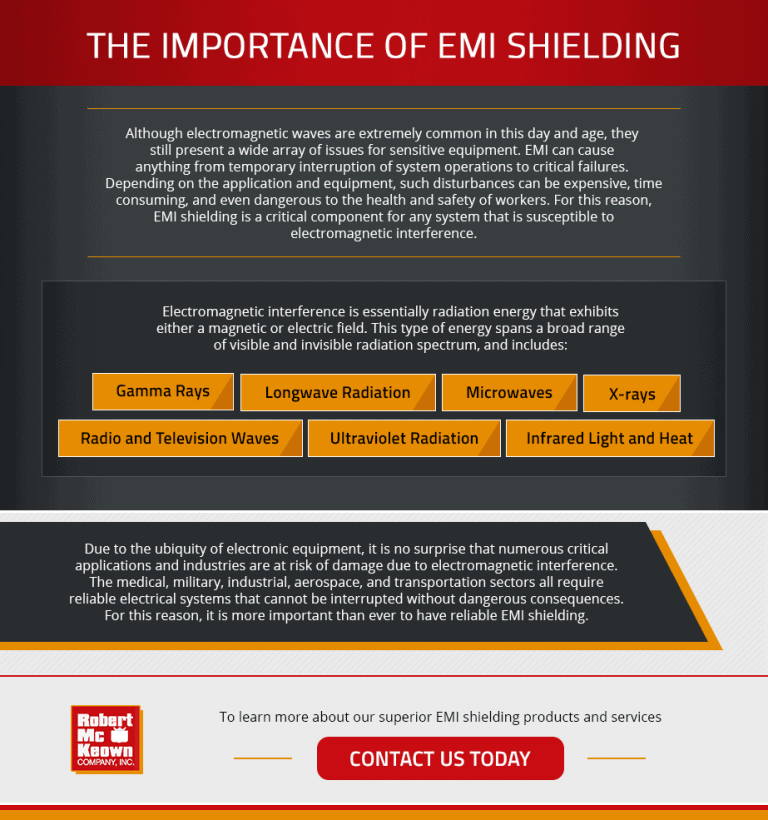
Understanding EMI Shielding
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding uses electrically conductive or magnetic materials to block electromagnetic interference in a given area. Electromagnetic interference can occur naturally in the form of solar flares, lightning, and aurora borealis. It is also caused by human activity such as cell phone signals, engine ignition switches, computers, and electrical equipment.
Due to the widespread use of sensitive electronic equipment for everything from transportation to banking and utility infrastructure, it is more important than ever to ensure the safety of electronic systems through the use of EMI shielding products and dedicated techniques. With the proper EMI protection, electronic systems will remain reliable and dependable in the face of both natural and man-made electronic interference.
THE IMPORTANCE OF SHIELDING
Although electromagnetic waves are extremely common in this day and age, they still present a wide array of issues for sensitive equipment. EMI can cause anything from temporary interruption of system operations to critical failures. Depending on the application and equipment, such disturbances can be expensive, time consuming, and even dangerous to the health and safety of workers. For this reason, EMI shielding is a critical component for any system that is susceptible to electromagnetic interference.
Electromagnetic interference is essentially radiation energy that exhibits either a magnetic or electric field. This type of energy spans a broad range of visible and invisible radiation spectrum, and includes:
- Gamma rays
- Longwave radiation
- Microwaves
- X-rays
- Radio and television waves
- Ultraviolet radiation
- Infrared light and heat
Due to the ubiquity of electronic equipment, it is no surprise that numerous critical applications and industries are at risk of damage due to electromagnetic interference. The medical, military, industrial, aerospace, and transportation sectors all require reliable electrical systems that cannot be interrupted without dangerous consequences. For this reason, it is more important than ever to have reliable EMI shielding.
BREAKING DOWN THE BIG PICTURE
EMI shielding comes in a variety of materials and designs, and can be engineered to meet the needs of specific equipment and applications. Components that may be modified for use in EMI shielding arrays include gaskets, wires, tapes, metal screens, and laminates, among many others. It is important to select the right material for the application to ensure optimal shielding of radiation at the correct wavelengths.
Some of the most common materials used in EMI shielding include:
STEEL ALLOYS
Carbon steel is often used in EMI shielding equipment, due to its exceptional strength and durability. It serves as an excellent shielding material for low-frequency magnetic waves, but can be heavier than other shielding materials and is susceptible to corrosion and oxidation. As an alternative, galvanized steel is an inexpensive and widely used shielding material that has been heat treated and exhibits a protective coating to prevent rust and corrosion.
ALUMINUM
Like galvanized steel, aluminum is less expensive than other shielding materials. Aluminum is lightweight, strong, and highly conductive, which makes it particularly useful for blocking a wide range of electronic waves. Of note, however, it is less effective than steel for protection against low-frequency electromagnetic radiation.
COPPER
Copper is by far the most popular EMI shielding material for radio and magnetic frequencies. It is highly conductive and easily formable, and easily absorbs magnetic, radio, and electrical waves. Although it is highly effective as a shielding material, pure copper may erode when exposed to certain elements in air and water.
COPPER ALLOY 770
To mitigate pure copper’s susceptibility to oxidation, Copper Alloy 770, a blend of copper, nickel, and zinc, is often used for EMI shielding products. Copper Alloy 770 exhibits similar radio and magnetic wave absorption without the potential for corrosion.
TIN-PLATED STEEL
Tin-plated steel is a popular inexpensive EMI shielding material that is ideal for radiation in low kHz and GHz frequencies. Like plain carbon steel, tin-plated steel protects equipment from low-frequency magnetic waves with the added benefit of corrosion protection. In addition to enhancing the material’s corrosion resistance, tin plating can easily be soldered to system components.
QUALITY EMI SHIELDING FROM ROBERT MCKEOWN
At Robert McKeown, we know that electromagnetic interference can have lasting negative effects on electronic equipment. We are dedicated to providing the highest quality EMI shielding solutions for reliable, long-lasting protection of your electronic systems. To learn more about our superior EMI shielding products and services, contact us today or request a quote.
Robert Mckeown’s COVID19 Statement to Customers
Dear Valued Customer,
Over the past several weeks we have dealt with an unprecedented challenge and have responded professionally to maintain the health and well-being of one another while maintaining the critical role we play in supporting our customers around the world.
The Robert McKeown Company is committed to the well being of all our employees and community. To reduce the impact of COVID-19 we have taken steps to transition staff offsite while protecting our in-house production and shipping staff.
Our business is classified as “essential” due to the military and other markets that we serve. As a result, we are allowed to continue operating. Our goal is to support the supply chain and movement of critical goods.
We will continue to monitor direction from state and federal government related to declarations of state emergency orders and are prepared to support those directives as required.
We appreciate your business and patience during this difficult time and will keep you updated on any changes as the situation continues to evolve.
Please call us should you have any concerns or questions.
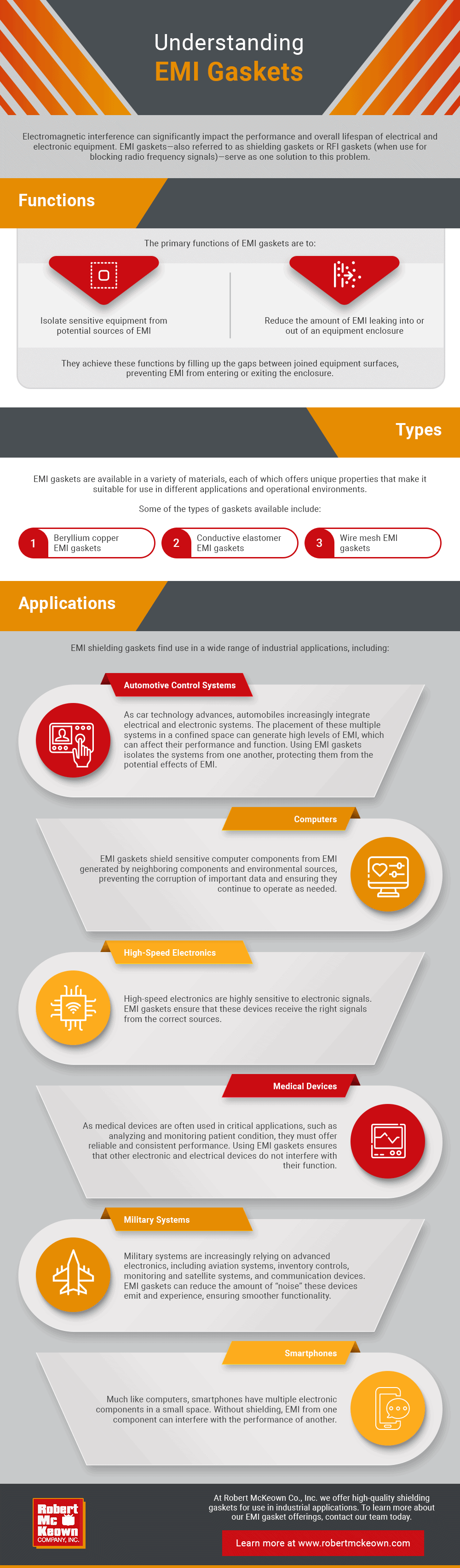
Protect Electrical and Electronic Equipment With EMI Gaskets
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can significantly impact the performance and overall lifespan of electrical and electronic equipment. EMI gaskets—also referred to as shielding gaskets or RFI gaskets (when use for blocking radio frequency signals)—serve as one solution to this problem. These devices physically close gaps in equipment enclosures to seal in or seal out EMI produced by the equipment or surrounding environment, respectively.
Typically made from metal, elastomers, or wire mesh, their critical function makes them essential for any industry that employs sensitive electrical and electronic devices. However, choosing one for an EMI shielding application can be challenging as it often necessitates an understanding of how they work and the types available to ensure optimal performance.
To facilitate the EMI gasket selection process for our customers, we’ve put together the following blog post, which outlines how EMI gaskets function, the types available, and their industrial applications.
FUNCTIONS OF EMI GASKETS
The primary functions of EMI gaskets are to:
- Isolate sensitive equipment from potential sources of EMI
- Reduce the amount of EMI leaking into or out of an equipment enclosure
They achieve these functions by filling up the gaps between joined equipment surfaces, preventing EMI from entering or exiting the enclosure.
TYPES OF EMI GASKETS
When choosing an EMI gasket for an electrical or electronic application, material is a key factor to keep in mind. EMI gaskets are available in a variety of materials, each of which offers unique properties that make it suitable for use in different applications and operational environments.
Some of the types of gaskets available include:
- Beryllium copper EMI gaskets. Copper is highly conductive, and beryllium copper is highly versatile. When used for EMI gaskets, these qualities combined make for superior performance and suitability for formation into custom shapes and sizes.
- Conductive elastomer EMI gaskets. Similar to beryllium copper gaskets, these gaskets are high-performing. Made from elastomer material, such as silicone and other rubbers, and often embedded with metallic components, they require pressure to form an adequate EMI shield.
- Wire mesh EMI gaskets. Wire mesh EMI gaskets can create permanent seals and provide high levels of shielding. However, they do not include an environmental seal element.
INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS OF EMI GASKETS
EMI shielding gaskets find use in a wide range of industrial applications, including:
- Automotive control systems. As car technology advances, automobiles increasingly integrate electrical and electronic systems, including ones for control, navigation, communication, and media. The placement of these multiple systems in a confined space can generate high levels of EMI, which can affect their performance and function. Using EMI gaskets isolates the systems from one another, protecting them from the potential effects of EMI.
- Computers. EMI gaskets shield sensitive computer components from EMI generated by neighboring components and environmental sources, preventing the corruption of important data and ensuring they continue to operate as needed.
- High-speed electronics. High-speed electronics are highly sensitive to electronic signals. EMI gaskets ensure that these devices receive the right signals from the correct sources.
- Medical devices. As medical devices are often used in critical applications, such as analyzing and monitoring patient condition, they must offer reliable and consistent performance. Using EMI gaskets ensures that other electronic and electrical devices do not interfere with their function.
- Military systems. Military systems are increasingly relying on advanced electronics, including aviation systems, inventory controls, monitoring and satellite systems, and communication devices. EMI gaskets can reduce the amount of “noise” these devices emit and experience, ensuring smoother functionality.
- Smartphones. Much like computers, smartphones have multiple electronic components in a small space. Without shielding, EMI from one component can interfere with the performance of another.
CONTACT THE SHIELDING GASKET EXPERTS AT ROBERT MCKEOWN TODAY
EMI gaskets protect sensitive electrical and electronic devices and systems from EMI. At Robert McKeown, we offer high-quality shielding gaskets for use in industrial applications. To learn more about our EMI gasket offerings, contact us or request a quote.
Protect Your Equipment and Employees With Shielding Tapes
The effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electrostatic discharge (ESD) can be devastating to sensitive electronic and electrical equipment and the employees that operate them. For example:
- EMI can ruin data collection and transmission, degrade signals, and interfere with or damage critical devices such as pacemakers.
- ESD can cause component failure and circuit destruction and result in electrical shock if the charge is not adequately dissipated.
Shielding products—such as shielding tapes—help disperse ESD and block EMI to minimize the risk of injury to life and limb and ensure the continued operation of the equipment. Shielding tapes act as a sealant. Instead of sealing in or out liquids, dirt, and other physical contaminants, they create a barrier that isolates the equipment and seals in or seals out EMI, ESD, and radio wave signals generated by environmental sources or the equipment itself.
Due to their critical function in electronic and electrical devices, shielding tapes find application in a wide range of industries, including medical and aerospace. Within these industries, companies employ EMI seals to protect their equipment and employees.
ADVANTAGES OF USING SHIELDING TAPE
When used in electronic and electrical systems for industrial applications, EMI shielding tape offers numerous advantages, including:
- Broader design flexibility and versatility. Shielding tapes are available in a variety of designs, materials, and sizes, which allows them to be tailored for use in a wide range of equipment and employee protection applications.
- Easier application and use. The application of EMI tape requires minimal surface preparation—i.e., ensuring the surface is dry and clean—and no specialized tools. As shielding tapes generally come with a pre-applied adhesive backing, they only require sufficient pressure to ensure adhesion to the equipment surface. As a grounding solution, the metallic part of the tape helps to disperse electrical charges safely without needing screws or other fasteners.
- Reduced crosstalk. Using these tapes reduces crosstalk—i.e., the interference of one signal by another nearby signal—across program or transmission channels.
- Greater protective properties. Shielding tapes minimize the adverse effects of ESD and ESI, resulting in greater protection for employees and equipment.
- Better durability. Many shielding tapes demonstrate superior abrasion and corrosion resistance and flame retardant properties, which enable them to withstand the stresses of use and result in longer service lives.
WHY WORK WITH SHIELDING TAPE EXPERTS?
With the numerous types of shielding tapes available, choosing the right one for a shielding application can be difficult. In these situations, it helps to get help. By consulting with an experienced fabricator and distributor of shielding tapes, customers receive qualified advice about which tape(s) is/are suitable for their needs or application and how best to apply it/them.
ORDER YOUR CUSTOM SHIELDING TAPES TODAY
Shielding products such as shielding tapes help protect your equipment and employees from EMI and ESD. At Robert McKeown, we offer shielding tapes and gaskets for use in industrial shielding applications. To further customize these EMI shielding products to our customers’ needs, we offer die cutting services.
To learn more about our EMI shielding tape and gasket offerings, contact us or request a quote.